Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a condition that affects the central part of the retina, called the macula, which is responsible for sharp, central vision. It is a leading cause of vision loss in people over 50 years of age.
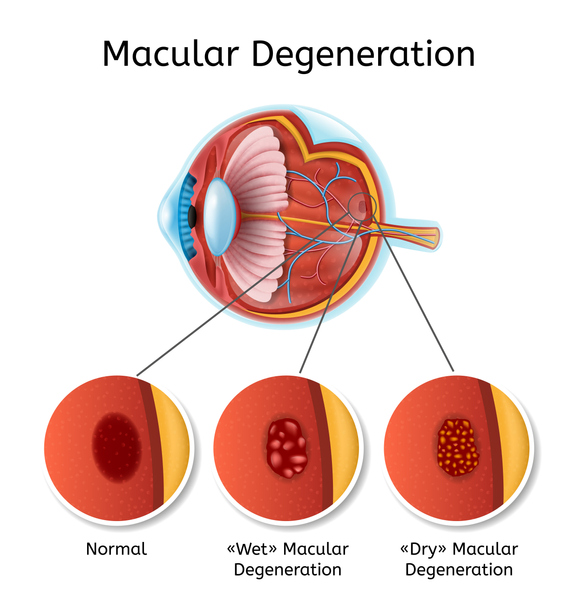
There are two types of AMD: dry AMD and wet AMD.
Dry AMD is much more common, accounting for about 90% of cases. It is estimated to affect more than 10 million people in the United States alone. Dry AMD is characterized by the presence of drusen - small yellow deposits that accumulate under the macula and cause damage over time.
Wet AMD, on the other hand, occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow under the macula and leak fluid and blood, causing more extensive injury. If left untreated, wet AMD often leads to permanent and severe vision loss, including legal blindness.
There are several risk factors associated with AMD, including age, family history, smoking, high blood pressure, and obesity. While some risk factors are beyond our control, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of AMD and slow its progression. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids
- Maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly
- Not smoking
- Monitoring and managing high blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Protecting the eyes from UV light by wearing sunglasses and a wide-brimmed hat when outdoors
- Getting regular eye exams, especially after the age of 50
Diagnostic Tests For AMD
A variety of tests are used to diagnose and monitor AMD. Your physician may perform any or all of the following:
- Dilated eye exam
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- OCT-angiography
- Fundus autofluorescence
- Fluorescein angiography
- Indocyanine green angiography
Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Wet AMD
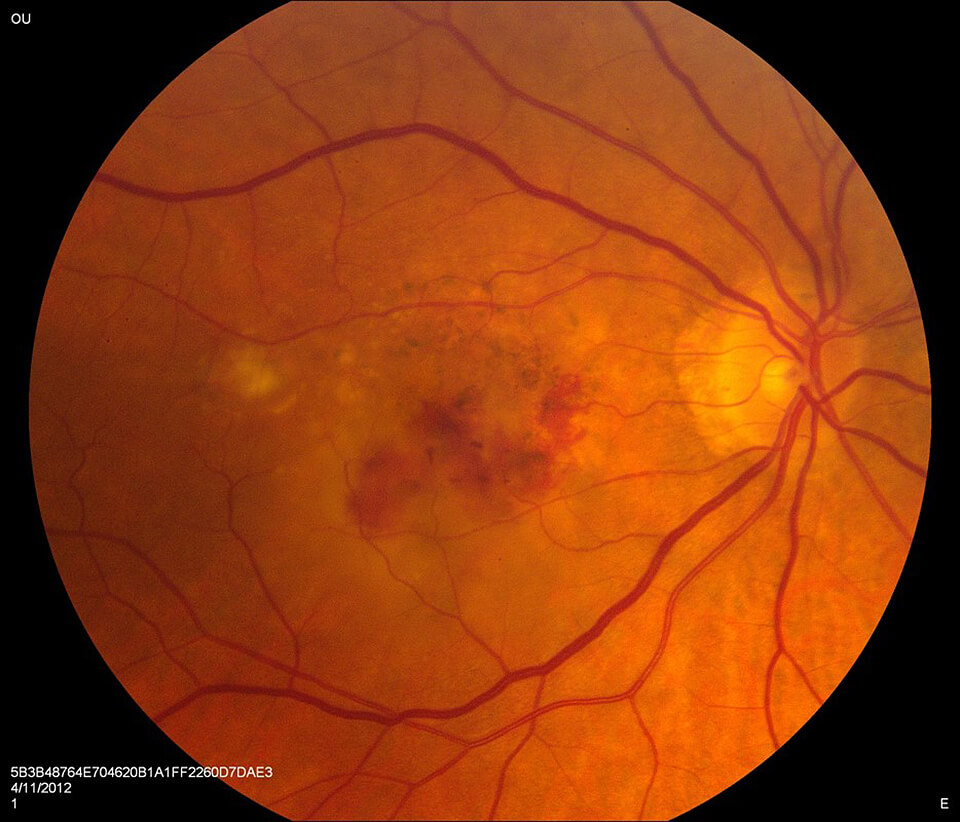
Injection of anti-VEGF medications into the eye is the primary treatment for wet AMD. These medications work by blocking the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina, thereby helping to preserve vision and slow disease progression. There are several available medications:
- Aflibercept (Eylea)
- Faricimab (Vabysmo)
- Ranibizumab (Cimerli, Byooviz, Lucentis)
- Bevacizumab (Avastin): originally developed as a cancer treatment and used off-label in the treatment of wet AMD and other eye conditions
Other management options for wet AMD that were used in the past include two different types of laser: Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) with verteporfin (Visudyne) and thermal laser. In current practice, these laser modalities are only used in select situations.
Dry AMD
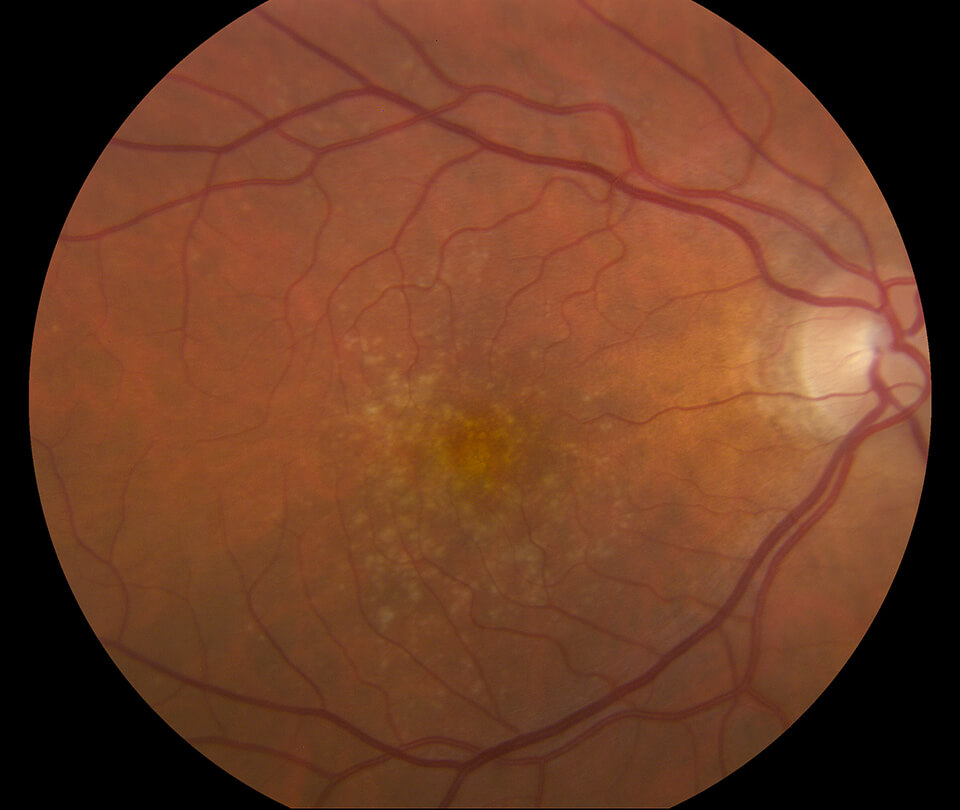
While there is currently no cure for dry AMD, there are various options that can help to slow its progression.
One of the most common options is vitamin supplementation with the Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS 2) formula. This formula has been shown to reduce the risk of disease progression to the advanced stages of AMD, particularly in people with intermediate or advanced AMD in one or both eyes.
The AREDS 2 formula comprises of:
- Vitamin C (500 mg)
- Vitamin E (400 IU)
- Copper (2 mg)
- Zinc (80 mg)
- Lutein (10 mg)
- Zeaxanthin (2 mg)
Another possible treatment for advanced dry AMD is Syfovre (pegcetacoplan), which is a medication given by intravitreal injection. Syfovre is used in the management of a particularly advanced form of dry AMD called geographic atrophy. This medication works by blocking the activity of the complement system, a part of the immune system that can cause damage to healthy cells, including those in the retina. In a clinical trial that led to its FDA approval, patients with geographic atrophy who received Syfovre had a significant reduction in the progression of disease compared to those who received a placebo. Despite these promising results, it is important to note that Syfovre does not reverse the atrophy that has already developed. Your retina specialist can help to determine if Syfovre is a suitable treatment option for you.
Clinical Research
The Retina Consultants of Minnesota has an active clinical trials department consisting of a team of experienced physicians, researchers, and support staff. Our goals are to improve patient outcomes and to contribute to the understanding of retinal diseases. We work with patients who have a wide range of retinal conditions, including those with age-related macular degeneration. We are involved in numerous national clinical trials that are evaluating the effectiveness of a variety of new treatments, including Eylea, Vabysmo, Avastin, Lucentis, Syfovre, and others. Our department collaborates with researchers from around the country, including those at academic centers, other retina practices, and pharmaceutical companies.
About Us
At Retina Consultants of Minnesota, we understand the impact that AMD can have on our patients' quality of life. We are committed to providing the highest quality care and using the latest technology to diagnose and treat AMD and other retinal conditions. If you or a loved one are experiencing changes in vision or have been diagnosed with AMD, we are here to help. Contact us today to schedule a consultation with one of our experienced retinal specialists.
Schedule a Consultation
To learn more about diabetic retinopathy, please call (855) 515-2020 to schedule a consultation.
We are proud to serve the communities of Minneapolis/St Paul, Brainerd, Duluth, Glencoe, Mankato, St. Cloud, and more.

